OATH - JUSTICE OF THE FUTURE

Introduction:Challenges associated with modern day dispute resolution systems
Sometimes they can cause irreparable damage to even the strongest relationship; and in other cases they tend to make them even stronger. Thus, in mutually beneficial relations (mainly business relations), both parties strive for the peaceful settlement of disputes in order to continue to reap the benefits of this mutual understanding.
Trials are not without their own tails, however. Settlement in court may take a long time before a decision is made due to delays, and the costs of hiring professional lawyers are extremely high, and in the case when both debaters agree, the problem of corruption and obstruction of justice time.
Aristotle once said that "he who controls the courts controls the states." This confirms the fact that legal systems are centralized, and individuals are in power. Such systems may be compromised by corruption and injustice in legal proceedings.
Finally, the number of small businesses is rapidly increasing. Unlike larger companies, they can generate revenue of a few hundred or thousands of dollars. In the event of a dispute arising from such meager amounts, what resolution method will be adopted in order to avoid costs, corruption, and loss of time associated with modern legal systems?
In this article, we will look in detail at Oath, a blockchain-based dispute resolution platform that uses the transparent nature of the blockchain, combined with the accuracy of intellectual contracts and a modified jury system to create an efficient, reliable, motivated and incorruptible dispute resolution ecosystem.
Often there are disputes between the parties to the transaction. As a result, it is recommended that the parties to the contract decide which funds will be used in the event of a dispute.
Oath offers a unique solution for resolving disputes between individuals and legal entities, providing a platform that allows the parties involved to enter into a smart contract that was developed using the jury system. Oath uses a new consensus mechanism, “Proof of Common Sense,” which allows the jury to manage cases using their common sense without requiring any previous experience in the field of contracts.
Number of jurors: A jury is a group of individuals who are chosen from among the public to decide on a particular case. When entering Oath developed a smart contract, the parties to the transaction must choose the number of jurors they want to preside over their disputes. They will also deposit a certain number of Oath tokens that will be used to pay for the presidency of the jury.
Court category: the court category allows Oath to select judges who are experts in the specified field in the event of a dispute. Thus, the parties involved need to select a category depending on the type of contract they are about to enter into.
Result: Various options or possible outcomes are created for the jury to choose from after the presiding judge. These possible results are agreed upon by the parties at the conclusion of the contract. For example, when settling a land dispute, the possible outcomes could be:
- Land ownership grant
- Grant of land ownership
- Sell the land and divide the income between parties A and B
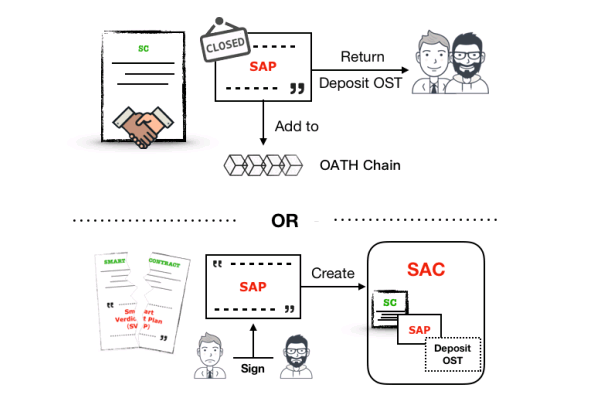
After all these details have been provided, the arbitration oath system is easily installed. In case of disagreement, disputants can easily submit a report with one touch of a button, while sending evidence to substantiate their claims. To this end, Oath immediately selects jurors in different parts of the world using the method that will be discussed in the next part of this article. If certain funds are involved in the dispute, the money is sent to the escrow account before the jury makes a decision. After receiving evidence, the jury is given a certain time to analyze the situation, and then make a decision by choosing one of the possible results specified in the contract.
The option most chosen by the jury is usually superior to others and is implemented accordingly in the contract.
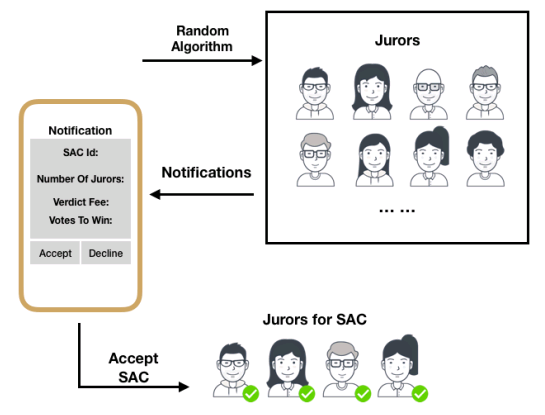
Jury selection
Jurors are often selected based on the categories specified in the smart contract. The categories provided by the contracting parties usually emphasize the preference of jurors with experience in the field of contracts so that they can make accurate and fair decisions. Depending on the number of jurors specified in a smart contract, a larger number can be randomly selected using the Oath algorithm, without taking into account the pre-set jury category.
After selection, jurors are notified with detailed information about the dispute, including the number of oath tokens with which they will be rewarded for leading the case. Based on this information, they can either accept or reject the case.
Arbitration
A jury receives remuneration for his work through arbitration fees, which are paid by one or both parties (depending on conditions in a smart contract). The reward system helps prevent bribery and corruption in the ecosystem.
Appeals
Appeals are very common in controversial cases. Many times one part feels dissatisfied with the decision and goes on to appeal. When this happens in the Oath ecosystem, a new business opens up, and this time with jurors with a higher level of credit. To control appeal levels, the appellant must pay an appeal fee and is limited to a maximum of two appeals, after which the sentence is sent to the smart contract.
In addition, appeals are beneficial because the jury in appeal cases withhold their payments pending an explanation of their decisions. This leads to more efficient and accurate solutions.
Appeals are a very effective mechanism to counter bribery, because, logically, new jurors remain unaware of previous sentences.
Justice through ratings and incentives
To ensure fairness in judgment, the ecosystem is built in such a way that jurors lose credit levels for dishonest decisions and win the opposite.
Lending levels are rating systems that largely determine the likelihood of choosing a juror, as well as payment for court decisions.
Use case
John is the happy owner of Wash n 'Folds Inc, a start-up company offering laundry services. In search of a logo that represents the company's services in a more visually appealing way, John continues to hire Kennedy, a graphic designer on the popular Independent Platform for doing work. They integrate their contract to the Oath platform, choosing four jurors, a category and some possible outcomes.
A week later, Kennedy finished the job and sent it to John as agreed. When John tries to place his new logo on a large billboard, he realizes that image quality declines when scaled to large size. He then complains to Kennedy, who explicitly refuses to make any changes to the task.
Immediately he calls for an oath dispute, sending proof of the negotiations with Kennedy, while Kennedy sends him in support of his claims. The jurors, who are also experts in graphic design, study the evidence and discover that John never requested a vector logo (which does not lose quality when scaled to large sizes), so three jurors decided that the Kennedy pixel logo should stand while only ruled against it.
According to the jury, John did not give a perfect description of his choice of logo, so Kennedy’s work was allowed, and his dedicated funds were effectively released.
Why oath?
- Low cost
- Less time compared to court decisions
- Incentive-based platform
- Keeps confidentiality of participants in the dispute.
- Less chance of obstructing justice
- Gives room for appeal
- Easily deploy smart contracts using custom templates
Conclusion
The need for a fast, secure and reliable dispute resolution mechanism has never been more obvious. The emergence of the digital world means an even greater increase in the number of business disputes, since millions of transactions are performed daily on the Internet. These and many other problems make Oath a unique and vivid solution to the problems at hand.
Road map
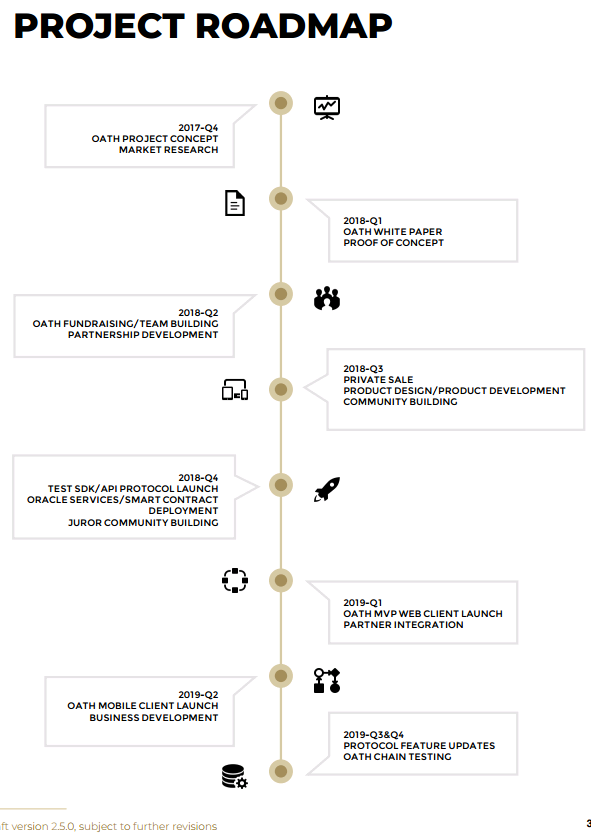
Links to official project resources:
Website: https://oathprotocol.com/en/
Telegram: https://t.me/oathsio
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/oathprotocol/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/OathProtocol
ETH: 0x10D894668E0fFb6142B8d72c8AA1BDa3702701B0


Komentar
Posting Komentar